springcloud中Hystrix指標收集原理是什么
這期內容當中小編將會給大家帶來有關spring cloud中Hystrix指標收集原理是什么,文章內容豐富且以專業的角度為大家分析和敘述,閱讀完這篇文章希望大家可以有所收獲。
成都創新互聯公司是專業的惠陽網站建設公司,惠陽接單;提供網站設計、成都做網站,網頁設計,網站設計,建網站,PHP網站建設等專業做網站服務;采用PHP框架,可快速的進行惠陽網站開發網頁制作和功能擴展;專業做搜索引擎喜愛的網站,專業的做網站團隊,希望更多企業前來合作!
hystrix運行原理
上一篇介紹了hystrix熔斷降級的基本實現原理,著重點是從hystrix自身的能力方面著手,結合代碼,做了整體介紹,那么觸發熔斷的指標是如何計算的,可能前面會籠統的提到metrics,至于它的metrics實現原理是怎么樣的,在本章做重點介紹
官方圖示: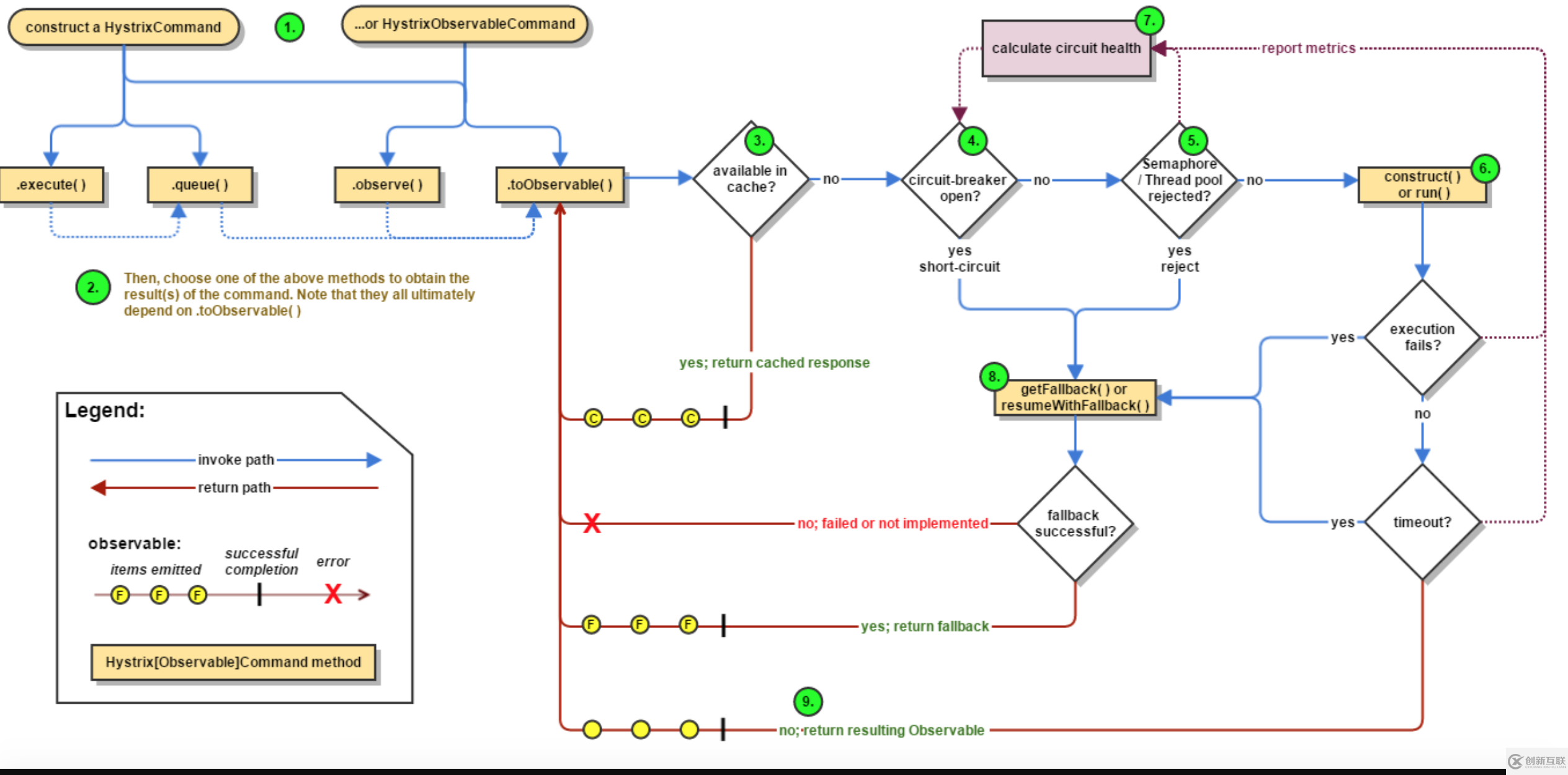
對于使用者先構造一個HystrixCommand對象或者HystrixObservalbeCommand
選擇queue或者execute,調用者決定是使用異步還是同步方式
根據commandKey看緩存中是否存在Observalbe,開啟緩存是為了提升性能,直接返回輸出
沒有緩存,那就開始走熔斷器的邏輯,先判斷熔斷器是不是開啟狀態
熔斷器開啟,觸發快速失敗,觸發降級,去執行用戶提供的fallback()邏輯
判斷是不是并發超限,超限,觸發降級,則發出執行拒絕的異常,去執行用戶提供的fallback邏輯
執行用戶實現的具體業務邏輯,是否出現執行異常或者超時,異常或超時,則觸發降級去執行用戶提供的fallback邏輯
執行結束
無論是正常結束還是執行異常,都會觸發metrics的收集,收集的結果經過計算后,提供給熔斷器,做開啟和關閉的決策
指標收集的實現
這部分我們需要從以下幾個方面做分析:指標上報、指標計算、指標使用,這期間會涉及多線程的并發寫入、消息的順序到達、滑動窗口的實現等等
指標上報
每一個請求線程,都會創建一個ExecutionResult實例,這個實例會關聯一些基礎事件比如開始時間、執行延遲、事件統計等基礎信息,也就是在整個hystrix的生命周期里面,會通過指標上報的方式做數據的收集,下面看下數據上報的幾個事件:
1.1、executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());//判斷斷路器未開啟,并發未超限,記錄執行的開始時間
1.2、executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.SUCCESS);//執行成功會增加success的事件和耗時
1.3、HystrixEventType.SHORT_CIRCUITED//斷路器打開,會收集快速熔斷的事件和耗時
1.4、HystrixEventType.SEMAPHORE_REJECTED//信號量方式并發數超限,會記錄該事件和耗時
1.5、HystrixEventType.THREAD_POOL_REJECTED//線程池不可用(并發超限),會記錄該事件和耗時
1.6、HystrixEventType.TIMEOUT//執行超時,會收集該事件和耗時
1.7、HystrixEventType.BAD_REQUEST//參數或狀態異常,會收集該事件和耗時
以上整體的事件分為兩大類,成功和失敗,根據用戶邏輯代碼的執行結果,如果是有異常,收集異常事件和耗時,執行circuitBreaker.markNonSuccess(),否則執行circuitBreaker.markNonSuccess()
另外觸發熔斷器開啟和關閉,有且只有兩個途徑,如下圖: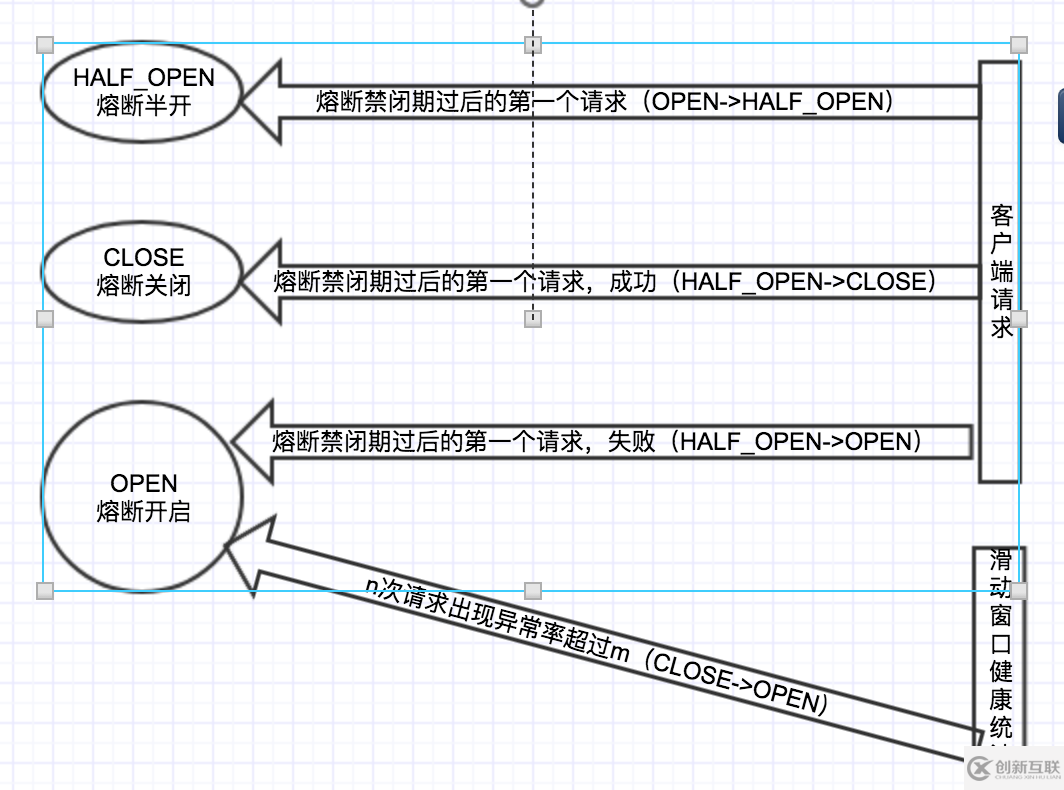
指標計算
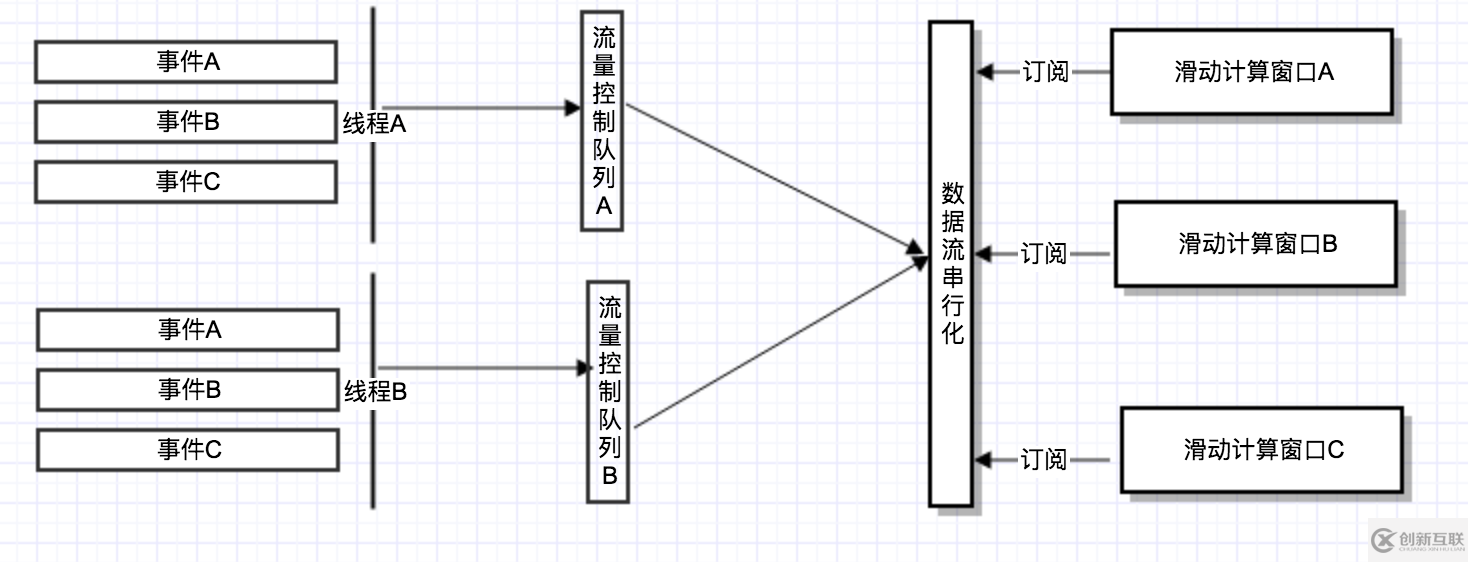
這里簡單對各個步驟中涉及到多線程并發的情況以及滑動窗口的計算做一個簡單介紹:
2.1:并發(threadLocal&SerializedSubject)
同一個接口收到多個請求時候,也就是這些請求命中的都是同一個commandKey時(統計指標是按照KEY為維度),每個請求都是一個獨立的線程,每個線程內會產生多個各種各樣的事件,首先同一個線程內的event拼接封裝成HystrixCommandCompletion,上報的是一個HystrixCommandCompletion,流計算操作的也是一個個的HystrixCommandCompletion,不存在計算時候把各線程的事件混雜在一起的可能,如何保證的在下面會講到
2.1.1:上報者是通過threadLocal線程隔離
首先hystrix啟動后會創建一個threadLocal,當一個客戶端請求不管是正常結束還是異常結束,都要上報上報狀態,也就是執行handleCommandEnd,都會從threadLocal中返回一個當前線程的HystrixThreadEventStream,代碼如下:private void handleCommandEnd(boolean commandExecutionStarted) { //省略部分代碼 if (executionResultAtTimeOfCancellation == null) { //上報metrics metrics.markCommandDone(executionResult, commandKey, threadPoolKey, commandExecutionStarted); } else { metrics.markCommandDone(executionResultAtTimeOfCancellation, commandKey, threadPoolKey, commandExecutionStarted); } }void markCommandDone(ExecutionResult executionResult, HystrixCommandKey commandKey, HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, boolean executionStarted) { //threadLocal中放置的是HystrixThreadEventStream,因為改寫了init方法,所以無需set,直接可以獲取 HystrixThreadEventStream.getInstance().executionDone(executionResult, commandKey, threadPoolKey); if (executionStarted) { concurrentExecutionCount.decrementAndGet(); } } //從threadLocal中獲取事件流 public static HystrixThreadEventStream getInstance() { return threadLocalStreams.get(); } //threadLocal的定義,改寫了init方法,所以不用單獨調用set private static final ThreadLocal<HystrixThreadEventStream> threadLocalStreams = new ThreadLocal<HystrixThreadEventStream>() { @Override protected HystrixThreadEventStream initialValue() { return new HystrixThreadEventStream(Thread.currentThread()); } }2.1.2:限流隊列
每個線程會有唯一的HystrixThreadEventStream,因為是從theadLocal獲取,每個HystrixThreadEventStream都會關聯一個由Subject實現的隊列,也就是每一個線程都有一個私有的隊列,這里說它提供限流是因為采用了‘背壓’的原理,所謂的‘背壓’是指按需提供,根據消費者的能力去往隊列生產,代碼如下:public void executionDone(ExecutionResult executionResult, HystrixCommandKey commandKey, HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey) { //把executionResult封裝成HystrixCommandCompletion,HystrixCommandCompletion是流計算操作的基本單位 HystrixCommandCompletion event = HystrixCommandCompletion.from(executionResult, commandKey, threadPoolKey); //writeOnlyCommandCompletionSubject就是一個通過RXjava實現的限流隊列 writeOnlyCommandCompletionSubject.onNext(event); } //省略代碼 writeOnlyCommandCompletionSubject .onBackpressureBuffer()//開啟'背壓功能' .doOnNext(writeCommandCompletionsToShardedStreams)//核心是這個action的call方法 .unsafeSubscribe(Subscribers.empty());2.2:數據流串行化
每個放入隊列的HystrixCommandCompletion,都會執利doOnNext的Action,通過他的call方法去調用HystrixCommandCompletionStream的write方法,相同的commandKey具有同一個HystrixCommandCompletionStream實例,具體是通過currentHashMap做的實例隔離,HystrixCommandCompletionStream內部是通過一個SerializedSubject實現多個HystrixCommandCompletion并行寫入的串行化,具體代碼邏輯如下://限流隊列收到數據后會執行call方法,是通過觀察者注冊了doOnnext事件 private static final Action1<HystrixCommandCompletion> writeCommandCompletionsToShardedStreams = new Action1<HystrixCommandCompletion>() { @Override public void call(HystrixCommandCompletion commandCompletion) { //同一個commandkey對應同一個串行隊列的實例,因為同一個commandKey必須要收集該key下所有線程的metrix事件做統計,才能準確 HystrixCommandCompletionStream commandStream = HystrixCommandCompletionStream.getInstance(commandCompletion.getCommandKey()); commandStream.write(commandCompletion);//寫入串行隊列,這里是核心 if (commandCompletion.isExecutedInThread() || commandCompletion.isResponseThreadPoolRejected()) { HystrixThreadPoolCompletionStream threadPoolStream = HystrixThreadPoolCompletionStream.getInstance(commandCompletion.getThreadPoolKey()); threadPoolStream.write(commandCompletion); } } }; //具體的write方法如下,需要重點關注writeOnlySubject的定義 public void write(HystrixCommandCompletion event) { writeOnlySubject.onNext(event); } //下面是writeOnlySubject的定義,是通過SerializedSubject將并行的寫入變為串行化 HystrixCommandCompletionStream(final HystrixCommandKey commandKey) { this.commandKey = commandKey; this.writeOnlySubject = new SerializedSubject<HystrixCommandCompletion, HystrixCommandCompletion>(PublishSubject.<HystrixCommandCompletion>create()); this.readOnlyStream = writeOnlySubject.share(); }2.3:消費訂閱
在hystrixCommand創建的時候,會對HystrixCommandCompletionStream進行訂閱,目前有:
healthCountsStream
rollingCommandEventCounterStream
cumulativeCommandEventCounterStream
rollingCommandLatencyDistributionStream
rollingCommandUserLatencyDistributionStream
rollingCommandMaxConcurrencyStream
這幾個消費者通過滾動窗口的形式,對數據做統計和指標計算,下面選取具有代表意義的healthCountsStream做講解:public static HealthCountsStream getInstance(HystrixCommandKey commandKey, HystrixCommandProperties properties) { //統計計算指標的時間間隔-metricsHealthSnapshotIntervalInMilliseconds final int healthCountBucketSizeInMs = properties.metricsHealthSnapshotIntervalInMilliseconds().get(); if (healthCountBucketSizeInMs == 0) { throw new RuntimeException("You have set the bucket size to 0ms. Please set a positive number, so that the metric stream can be properly consumed"); } //熔斷窗口滑動周期,默認10秒,保留10秒內的統計數據,指定窗口期內,有效進行指標計算的次數=metricsRollingStatisticalWindowInMilliseconds/metricsHealthSnapshotIntervalInMilliseconds final int numHealthCountBuckets = properties.metricsRollingStatisticalWindowInMilliseconds().get() / healthCountBucketSizeInMs; return getInstance(commandKey, numHealthCountBuckets, healthCountBucketSizeInMs); } //繼承關系HealthCountStream-》BucketedRollingCounterStream-》BucketedCounterStream //把各事件聚合成桶...省略代碼,在BucketedCounterStream完成 this.bucketedStream = Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<Bucket>>() { @Override public Observable<Bucket> call() { return inputEventStream .observe() .window(bucketSizeInMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) //bucket it by the counter window so we can emit to the next operator in time chunks, not on every OnNext .flatMap(reduceBucketToSummary) //for a given bucket, turn it into a long array containing counts of event types .startWith(emptyEventCountsToStart); //start it with empty arrays to make consumer logic as generic as possible (windows are always full) } } //聚合成桶的邏輯代碼 public static final Func2<long[], HystrixCommandCompletion, long[]> appendEventToBucket = new Func2<long[], HystrixCommandCompletion, long[]>() { @Override public long[] call(long[] initialCountArray, HystrixCommandCompletion execution) { ExecutionResult.EventCounts eventCounts = execution.getEventCounts(); for (HystrixEventType eventType: ALL_EVENT_TYPES) { switch (eventType) { case EXCEPTION_THROWN: break; //this is just a sum of other anyway - don't do the work here default: initialCountArray[eventType.ordinal()] += eventCounts.getCount(eventType);//對各類型的event做,分類匯總 break; } } return initialCountArray; } }; //生成計算指標,在BucketedRollingCounterStream完成,省略部分代碼 this.sourceStream = bucketedStream //stream broken up into buckets .window(numBuckets, 1) //emit overlapping windows of buckets .flatMap(reduceWindowToSummary) //convert a window of bucket-summaries into a single summary .doOnSubscribe(new Action0() { @Override public void call() { isSourceCurrentlySubscribed.set(true); } }) //計算指標聚合實現,reduceWindowToSummary private static final Func2<HystrixCommandMetrics.HealthCounts, long[], HystrixCommandMetrics.HealthCounts> healthCheckAccumulator = new Func2<HystrixCommandMetrics.HealthCounts, long[], HystrixCommandMetrics.HealthCounts>() { @Override public HystrixCommandMetrics.HealthCounts call(HystrixCommandMetrics.HealthCounts healthCounts, long[] bucketEventCounts) { return healthCounts.plus(bucketEventCounts);//重點看該方法 } }; public HealthCounts plus(long[] eventTypeCounts) { long updatedTotalCount = totalCount; long updatedErrorCount = errorCount; long successCount = eventTypeCounts[HystrixEventType.SUCCESS.ordinal()]; long failureCount = eventTypeCounts[HystrixEventType.FAILURE.ordinal()]; long timeoutCount = eventTypeCounts[HystrixEventType.TIMEOUT.ordinal()]; long threadPoolRejectedCount = eventTypeCounts[HystrixEventType.THREAD_POOL_REJECTED.ordinal()]; long semaphoreRejectedCount = eventTypeCounts[HystrixEventType.SEMAPHORE_REJECTED.ordinal()]; //多個線程的事件,被匯總計算以后,所有的事件相加得到總和 updatedTotalCount += (successCount + failureCount + timeoutCount + threadPoolRejectedCount + semaphoreRejectedCount); //失敗的事件總和,注意只有FAIL+timeoutCount+THREAD_POOL_REJECTED+SEMAPHORE_REJECTED updatedErrorCount += (failureCount + timeoutCount + threadPoolRejectedCount + semaphoreRejectedCount); return new HealthCounts(updatedTotalCount, updatedErrorCount); }指標使用
指標使用比較簡單,用于控制熔斷器的關閉與開啟,邏輯如下:public void onNext(HealthCounts hc) { if (hc.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get()) { } else { if (hc.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get()) { } else { if (status.compareAndSet(Status.CLOSED, Status.OPEN)) { circuitOpened.set(System.currentTimeMillis()); } } } }
上述就是小編為大家分享的spring cloud中Hystrix指標收集原理是什么了,如果剛好有類似的疑惑,不妨參照上述分析進行理解。如果想知道更多相關知識,歡迎關注創新互聯行業資訊頻道。
當前文章:springcloud中Hystrix指標收集原理是什么
本文鏈接:http://m.newbst.com/article16/jicgdg.html
成都網站建設公司_創新互聯,為您提供App設計、App開發、外貿網站建設、全網營銷推廣、用戶體驗、標簽優化
聲明:本網站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如需處理請聯系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創新互聯

- 網站建設規劃_電子商務網站建設規劃。 2021-11-01
- 電子商務網站建設的流程是什么? 2022-06-17
- 電子商務發展機遇與挑戰并存 2022-11-18
- 電子商務型網站建設重在細節 2015-06-14
- 農業電子商務網站建設實現農業信息的共享流通 2022-02-25
- 如何運用電子商務平臺做好推廣 2022-11-10
- 幫助您優化移動設備電子商務網站的8條提示 2022-07-17
- 電子商務的一般框架 2022-05-07
- 建設電子商務網站的基本要求是什么 2021-12-24
- 溫州網站建設-電子商務網站設計這些技巧 2021-10-22
- 電子商務解決方案---B2B 2021-05-16
- 分享電子商務網站產品頁SEO優化的六大禁忌 2022-06-04