如何在Android中利用GestureDetector進(jìn)行手勢(shì)檢測(cè)
今天就跟大家聊聊有關(guān)如何在Android中利用 GestureDetector進(jìn)行手勢(shì)檢測(cè),可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結(jié)了以下內(nèi)容,希望大家根據(jù)這篇文章可以有所收獲。
公司主營(yíng)業(yè)務(wù):網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、成都做網(wǎng)站、移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站開發(fā)等業(yè)務(wù)。幫助企業(yè)客戶真正實(shí)現(xiàn)互聯(lián)網(wǎng)宣傳,提高企業(yè)的競(jìng)爭(zhēng)能力。創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)建站是一支青春激揚(yáng)、勤奮敬業(yè)、活力青春激揚(yáng)、勤奮敬業(yè)、活力澎湃、和諧高效的團(tuán)隊(duì)。公司秉承以“開放、自由、嚴(yán)謹(jǐn)、自律”為核心的企業(yè)文化,感謝他們對(duì)我們的高要求,感謝他們從不同領(lǐng)域給我們帶來的挑戰(zhàn),讓我們激情的團(tuán)隊(duì)有機(jī)會(huì)用頭腦與智慧不斷的給客戶帶來驚喜。創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)建站推出北川羌族免費(fèi)做網(wǎng)站回饋大家。
一、概述
當(dāng)用戶觸摸屏幕的時(shí)候,會(huì)產(chǎn)生許多手勢(shì),例如down,up,scroll,filing等等。
一般情況下,我們知道View類有個(gè)View.OnTouchListener內(nèi)部接口,通過重寫他的onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event)方法,我們可以處理一些touch事件,但是這個(gè)方法太過簡(jiǎn)單,如果需要處理一些復(fù)雜的手勢(shì),用這個(gè)接口就會(huì)很麻煩(因?yàn)槲覀円约焊鶕?jù)用戶觸摸的軌跡去判斷是什么手勢(shì))。
Android sdk給我們提供了GestureDetector(Gesture:手勢(shì)Detector:識(shí)別)類,通過這個(gè)類我們可以識(shí)別很多的手勢(shì),主要是通過他的onTouchEvent(event)方法完成了不同手勢(shì)的識(shí)別。雖然他能識(shí)別手勢(shì),但是不同的手勢(shì)要怎么處理,應(yīng)該是提供給程序員實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
GestureDetector這個(gè)類對(duì)外提供了兩個(gè)接口和一個(gè)外部類
接口:OnGestureListener,OnDoubleTapListener
內(nèi)部類:SimpleOnGestureListener
這個(gè)外部類,其實(shí)是兩個(gè)接口中所有函數(shù)的集成,它包含了這兩個(gè)接口里所有必須要實(shí)現(xiàn)的函數(shù)而且都已經(jīng)重寫,但所有方法體都是空的;不同點(diǎn)在于:該類是static class,程序員可以在外部繼承這個(gè)類,重寫里面的手勢(shì)處理方法。
下面我們先看OnGestureListener接口;
二、GestureDetector.OnGestureListener---接口
1、基本講解
如果我們寫一個(gè)類并implements OnGestureListener,會(huì)提示有幾個(gè)必須重寫的函數(shù),加上之后是這個(gè)樣子的:
private class gesturelistener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}可見,這里總共重寫了六個(gè)函數(shù),這些函數(shù)都在什么情況下才會(huì)觸發(fā)呢,下面講一下:
OnDown(MotionEvent e):用戶按下屏幕就會(huì)觸發(fā);
onShowPress(MotionEvent e):如果是按下的時(shí)間超過瞬間,而且在按下的時(shí)候沒有松開或者是拖動(dòng)的,那么onShowPress就會(huì)執(zhí)行,具體這個(gè)瞬間是多久,我也不清楚呃……
onLongPress(MotionEvent e):長(zhǎng)按觸摸屏,超過一定時(shí)長(zhǎng),就會(huì)觸發(fā)這個(gè)事件
觸發(fā)順序:
onDown->onShowPress->onLongPress
onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e):從名子也可以看出,一次單獨(dú)的輕擊抬起操作,也就是輕擊一下屏幕,立刻抬起來,才會(huì)有這個(gè)觸發(fā),當(dāng)然,如果除了Down以外還有其它操作,那就不再算是Single操作了,所以也就不會(huì)觸發(fā)這個(gè)事件
觸發(fā)順序:
點(diǎn)擊一下非常快的(不滑動(dòng))Touchup:
onDown->onSingleTapUp->onSingleTapConfirmed
點(diǎn)擊一下稍微慢點(diǎn)的(不滑動(dòng))Touchup:
onDown->onShowPress->onSingleTapUp->onSingleTapConfirmed
onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,float velocityY) :滑屏,用戶按下觸摸屏、快速移動(dòng)后松開,由1個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多個(gè)ACTION_MOVE, 1個(gè)ACTION_UP觸發(fā)
參數(shù)解釋:
e1:第1個(gè)ACTION_DOWN MotionEvent
e2:最后一個(gè)ACTION_MOVE MotionEvent
velocityX:X軸上的移動(dòng)速度,像素/秒
velocityY:Y軸上的移動(dòng)速度,像素/秒
onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,float distanceX, float distanceY):在屏幕上拖動(dòng)事件。無(wú)論是用手拖動(dòng)view,或者是以拋的動(dòng)作滾動(dòng),都會(huì)多次觸發(fā),這個(gè)方法在ACTION_MOVE動(dòng)作發(fā)生時(shí)就會(huì)觸發(fā)
滑屏:手指觸動(dòng)屏幕后,稍微滑動(dòng)后立即松開
onDown-----》onScroll----》onScroll----》onScroll----》………----->onFling
拖動(dòng):
onDown------》onScroll----》onScroll------》onFiling
可見,無(wú)論是滑屏,還是拖動(dòng),影響的只是中間OnScroll觸發(fā)的數(shù)量多少而已,最終都會(huì)觸發(fā)onFling事件!
2、實(shí)例
要使用GestureDetector,有三步要走:
1.創(chuàng)建OnGestureListener監(jiān)聽函數(shù):
可以使用構(gòu)造實(shí)例:
GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener = new GestureDetector.OnGestureListener(){
};也可以構(gòu)造類:
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
}2.創(chuàng)建GestureDetector實(shí)例mGestureDetector:
構(gòu)造函數(shù)有下面三個(gè),根據(jù)需要選擇:
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener);
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener);
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener listener);
3、onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event)中攔截:
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}4.控件綁定
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv); tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
現(xiàn)在進(jìn)入實(shí)例階段:
首先,在主布局頁(yè)面添加一個(gè)textView,并將其放大到整屏,方便在其上的手勢(shì)識(shí)別,代碼為:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.gesturedetectorinterface.MainActivity" > <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_margin="50dip" android:background="#ff00ff" android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>
然后在JAVA代碼中,依據(jù)上面的三步走原則,寫出代碼,并在所有的手勢(shì)下添加上Toast提示并寫上Log
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener{
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new gestureListener()); //使用派生自O(shè)nGestureListener
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
/*
* 在onTouch()方法中,我們調(diào)用GestureDetector的onTouchEvent()方法,將捕捉到的MotionEvent交給GestureDetector
* 來分析是否有合適的callback函數(shù)來處理用戶的手勢(shì)
*/
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
// 用戶輕觸觸摸屏,由1個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN觸發(fā)
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false;
}
/*
* 用戶輕觸觸摸屏,尚未松開或拖動(dòng),由一個(gè)1個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN觸發(fā)
* 注意和onDown()的區(qū)別,強(qiáng)調(diào)的是沒有松開或者拖動(dòng)的狀態(tài)
*
* 而onDown也是由一個(gè)MotionEventACTION_DOWN觸發(fā)的,但是他沒有任何限制,
* 也就是說當(dāng)用戶點(diǎn)擊的時(shí)候,首先MotionEventACTION_DOWN,onDown就會(huì)執(zhí)行,
* 如果在按下的瞬間沒有松開或者是拖動(dòng)的時(shí)候onShowPress就會(huì)執(zhí)行,如果是按下的時(shí)間超過瞬間
* (這塊我也不太清楚瞬間的時(shí)間差是多少,一般情況下都會(huì)執(zhí)行onShowPress),拖動(dòng)了,就不執(zhí)行onShowPress。
*/
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
// 用戶(輕觸觸摸屏后)松開,由一個(gè)1個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_UP觸發(fā)
///輕擊一下屏幕,立刻抬起來,才會(huì)有這個(gè)觸發(fā)
//從名子也可以看出,一次單獨(dú)的輕擊抬起操作,當(dāng)然,如果除了Down以外還有其它操作,那就不再算是Single操作了,所以這個(gè)事件 就不再響應(yīng)
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapUp", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
// 用戶按下觸摸屏,并拖動(dòng),由1個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多個(gè)ACTION_MOVE觸發(fā)
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture22", "onScroll:"+(e2.getX()-e1.getX()) +" "+distanceX);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
// 用戶長(zhǎng)按觸摸屏,由多個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN觸發(fā)
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
// 用戶按下觸摸屏、快速移動(dòng)后松開,由1個(gè)MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多個(gè)ACTION_MOVE, 1個(gè)ACTION_UP觸發(fā)
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
};
}源碼在博客底部給出。
三、GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener---接口
1、構(gòu)建
有兩種方式設(shè)置雙擊監(jiān)聽:
方法一:新建一個(gè)類同時(shí)派生自O(shè)nGestureListener和OnDoubleTapListener:
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener,GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
}方法二:使用GestureDetector::setOnDoubleTapListener();函數(shù)設(shè)置監(jiān)聽:
//構(gòu)建GestureDetector實(shí)例
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new gestureListener()); //使用派生自O(shè)nGestureListener
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
}
//設(shè)置雙擊監(jiān)聽器
mGestureDetector.setOnDoubleTapListener(new doubleTapListener());
private class doubleTapListener implements GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
}注意:大家可以看到無(wú)論在方法一還是在方法二中,都需要派生自GestureDetector.OnGestureListener,前面我們說過GestureDetector 的構(gòu)造函數(shù),如下:
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener);
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener);
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener listener);
可以看到,在構(gòu)造函數(shù)中,除了后面要講的SimpleOnGestureListener 以外的其它兩個(gè)構(gòu)造函數(shù)都必須是OnGestureListener的實(shí)例。所以要想使用OnDoubleTapListener的幾個(gè)函數(shù),就必須先實(shí)現(xiàn)OnGestureListener。
2、函數(shù)講解
首先看一下OnDoubleTapListener接口必須重寫的三個(gè)函數(shù):
private class doubleTapListener implements GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e):單擊事件。用來判定該次點(diǎn)擊是SingleTap而不是DoubleTap,如果連續(xù)點(diǎn)擊兩次就是DoubleTap手勢(shì),如果只點(diǎn)擊一次,系統(tǒng)等待一段時(shí)間后沒有收到第二次點(diǎn)擊則判定該次點(diǎn)擊為SingleTap而不是DoubleTap,然后觸發(fā)SingleTapConfirmed事件。觸發(fā)順序是:OnDown->OnsingleTapUp->OnsingleTapConfirmed
關(guān)于onSingleTapConfirmed和onSingleTapUp的一點(diǎn)區(qū)別: OnGestureListener有這樣的一個(gè)方法onSingleTapUp,和onSingleTapConfirmed容易混淆。二者的區(qū)別是:onSingleTapUp,只要手抬起就會(huì)執(zhí)行,而對(duì)于onSingleTapConfirmed來說,如果雙擊的話,則onSingleTapConfirmed不會(huì)執(zhí)行。
onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e):雙擊事件
onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e):雙擊間隔中發(fā)生的動(dòng)作。指觸發(fā)onDoubleTap以后,在雙擊之間發(fā)生的其它動(dòng)作,包含down、up和move事件;下圖是雙擊一下的Log輸出:
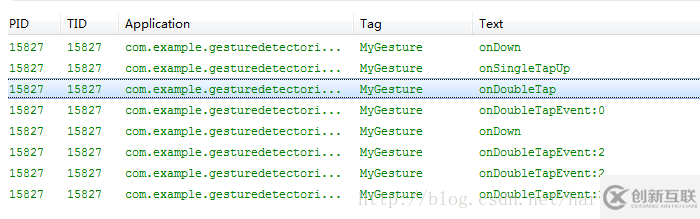
兩點(diǎn)總結(jié):
1、從上圖可以看出,在第二下點(diǎn)擊時(shí),先觸發(fā)OnDoubleTap,然后再觸發(fā)OnDown(第二次點(diǎn)擊)
2、其次在觸發(fā)OnDoubleTap以后,就開始觸發(fā)onDoubleTapEvent了,onDoubleTapEvent后面的數(shù)字代表了當(dāng)前的事件,0指ACTION_DOWN,1指ACTION_UP,2 指ACTION_MOVE
在上一個(gè)例子的基礎(chǔ)上,我們?cè)偬砑右粋€(gè)雙擊監(jiān)聽類,實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener{
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new gestureListener()); //使用派生自O(shè)nGestureListener
mGestureDetector.setOnDoubleTapListener(new doubleTapListener());
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
/*
* 在onTouch()方法中,我們調(diào)用GestureDetector的onTouchEvent()方法,將捕捉到的MotionEvent交給GestureDetector
* 來分析是否有合適的callback函數(shù)來處理用戶的手勢(shì)
*/
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
//OnGestureListener監(jiān)聽
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapUp", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture22", "onScroll:"+(e2.getX()-e1.getX()) +" "+distanceX);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
};
//OnDoubleTapListener監(jiān)聽
private class doubleTapListener implements GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapConfirmed");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapConfirmed", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTap");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTap", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTapEvent");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTapEvent", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
};
}雙擊一下,部分截圖如下:
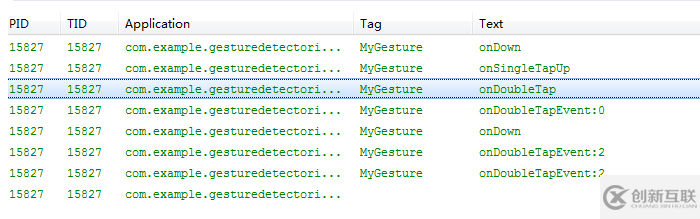
雙擊所對(duì)應(yīng)的觸發(fā)事件順序:
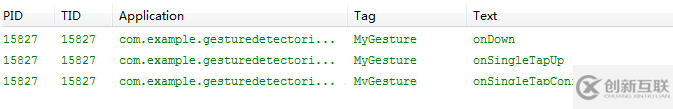
輕輕單擊一下,對(duì)應(yīng)的事件觸發(fā)順序?yàn)椋?/p>
源碼在博客底部給出。
四、GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener---類
它與前兩個(gè)不同的是:
1、這是一個(gè)類,在它基礎(chǔ)上新建類的話,要用extends派生而不是用implements繼承!
2、OnGestureListener和OnDoubleTapListener接口里的函數(shù)都是強(qiáng)制必須重寫的,即使用不到也要重寫出來一個(gè)空函數(shù)但在SimpleOnGestureListener類的實(shí)例或派生類中不必如此,可以根據(jù)情況,用到哪個(gè)函數(shù)就重寫哪個(gè)函數(shù),因?yàn)镾impleOnGestureListener類本身已經(jīng)實(shí)現(xiàn)了這兩個(gè)接口的所有函數(shù),只是里面全是空的而已。
下面利用SimpleOnGestureListener類來重新實(shí)現(xiàn)上面的幾個(gè)效果,代碼如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new simpleGestureListener());
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private class simpleGestureListener extends
GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener {
/*****OnGestureListener的函數(shù)*****/
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapUp",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onScroll:" + (e2.getX() - e1.getX()) + " "
+ distanceX);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
return true;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
return true;
}
/*****OnDoubleTapListener的函數(shù)*****/
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapConfirmed");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapConfirmed",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTap");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTap", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTapEvent");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTapEvent",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
}
}到此,有關(guān)GestureDetector的所有基礎(chǔ)知識(shí)都講解完了,下面給出一個(gè)小應(yīng)用——識(shí)別用戶是向左滑還是向右滑!
源碼在博客底部給出。
五、OnFling應(yīng)用——識(shí)別向左滑還是向右滑
這部分就有點(diǎn)意思了,可以說是上面知識(shí)的一個(gè)小應(yīng)用,我們利用OnFling函數(shù)來識(shí)別當(dāng)前用戶是在向左滑還是向右滑,從而打出日志。先看下OnFling的參數(shù):
boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,float velocityY)
參數(shù)解釋:
e1:第1個(gè)ACTION_DOWN MotionEvent
e2:最后一個(gè)ACTION_MOVE MotionEvent
velocityX:X軸上的移動(dòng)速度,像素/秒
velocityY:Y軸上的移動(dòng)速度,像素/秒
首先,先說一下實(shí)現(xiàn)的功能:當(dāng)用戶向左滑動(dòng)距離超過100px,且滑動(dòng)速度超過100 px/s時(shí),即判斷為向左滑動(dòng);向右同理.代碼如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new simpleGestureListener());
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private class simpleGestureListener extends
GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener {
/*****OnGestureListener的函數(shù)*****/
final int FLING_MIN_DISTANCE = 100, FLING_MIN_VELOCITY = 200;
// 觸發(fā)條件 :
// X軸的坐標(biāo)位移大于FLING_MIN_DISTANCE,且移動(dòng)速度大于FLING_MIN_VELOCITY個(gè)像素/秒
// 參數(shù)解釋:
// e1:第1個(gè)ACTION_DOWN MotionEvent
// e2:最后一個(gè)ACTION_MOVE MotionEvent
// velocityX:X軸上的移動(dòng)速度,像素/秒
// velocityY:Y軸上的移動(dòng)速度,像素/秒
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
if (e1.getX() - e2.getX() > FLING_MIN_DISTANCE
&& Math.abs(velocityX) > FLING_MIN_VELOCITY) {
// Fling left
Log.i("MyGesture", "Fling left");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Fling Left", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else if (e2.getX() - e1.getX() > FLING_MIN_DISTANCE
&& Math.abs(velocityX) > FLING_MIN_VELOCITY) {
// Fling right
Log.i("MyGesture", "Fling right");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Fling Right", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
return true;
}
}
}看完上述內(nèi)容,你們對(duì)如何在Android中利用 GestureDetector進(jìn)行手勢(shì)檢測(cè)有進(jìn)一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識(shí)或者相關(guān)內(nèi)容,請(qǐng)關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
文章名稱:如何在Android中利用GestureDetector進(jìn)行手勢(shì)檢測(cè)
鏈接URL:http://m.newbst.com/article28/jesjjp.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供面包屑導(dǎo)航、網(wǎng)站維護(hù)、品牌網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、ChatGPT、微信公眾號(hào)、定制開發(fā)
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 跨平臺(tái)移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)開發(fā)框架介紹 2023-02-26
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的意義以及重要性 2016-10-06
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的注意事項(xiàng)有哪些? 2023-01-10
- 房產(chǎn)門戶網(wǎng)站建設(shè)必須留意的事宜 2016-11-15
- 企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的基本功能及報(bào)價(jià) 2021-05-31
- 做好企業(yè)營(yíng)銷網(wǎng)站建設(shè)需要掌握哪些細(xì)節(jié)? 2016-10-05
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)之英語(yǔ)版網(wǎng)站需要注意的事情 2016-08-12
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)首頁(yè)設(shè)計(jì) 5個(gè)方案選擇 2018-05-09
- 從哪些方面挑選成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)開發(fā)公司 2023-02-21
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)與推廣完美結(jié)合 2021-05-24
- 只有弄清楚網(wǎng)站類型并有的放矢才能做好網(wǎng)站建設(shè)工作 2022-05-16
- 成都外貿(mào)企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)做好這三點(diǎn)勢(shì)必推動(dòng)網(wǎng)站轉(zhuǎn)化 2016-03-13