查漏補缺:連接器在Tomcat中是如何設計的
2021-02-23 分類: 網站建設
從連接器(Connector)源碼說起

既然是來解析連接器(Connector),那么我們直接從源碼入手,后面所有源碼我會剔除不重要部分,所以會忽略大部分源碼細節,只關注流程。源碼如下(高能預警,大量代碼):
- public class Connector extends LifecycleMBeanBase {
- public Connector() {
- this("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol");
- }
- public Connector(String protocol) {
- boolean aprConnector = AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() &&
- AprLifecycleListener.getUseAprConnector();
- if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol) || protocol == null) {
- if (aprConnector) {
- protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol";
- } else {
- protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol";
- }
- } else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) {
- if (aprConnector) {
- protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol";
- } else {
- protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol";
- }
- } else {
- protocolHandlerClassName = protocol;
- }
- // Instantiate protocol handler
- ProtocolHandler p = null;
- try {
- Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocolHandlerClassName);
- p = (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- log.error(sm.getString(
- "coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
- } finally {
- this.protocolHandler = p;
- }
- // Default for Connector depends on this system property
- setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
- }
我們來看看Connector的構造方法,其實只做了一件事情,就是根據協議設置對應的ProtocolHandler,根據名稱我們知道,這是協議處理類,所以連接器內部的一個重要子模塊就是ProtocolHandler。
關于生命周期
我們看到Connector繼承了LifecycleMBeanBase,我們來看看Connector的最終繼承關系:
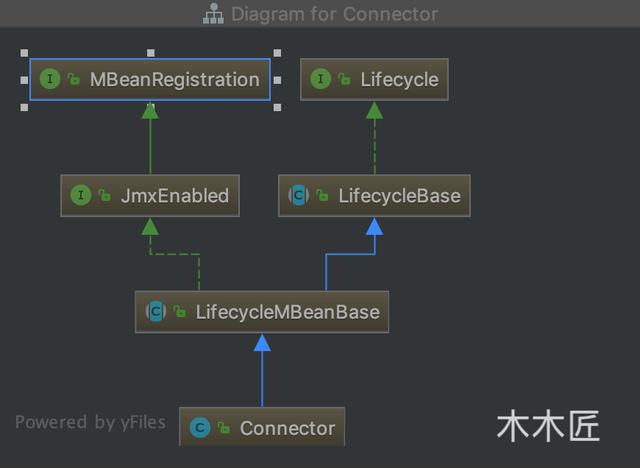
我們看到最終實現的是Lifecycle接口,我們看看這個接口是何方神圣。我把其接口的注釋拿下來解釋下
這段注釋翻譯就是,這個接口是提供給組件聲明周期管理的,并且提供了聲明周期流轉圖。這里我們只需要知道正常流程即可:
- New--->Init()---->Start()---->Stop()--->Destory()
從生命周期探索連接器
根據上面的生命周期說明,我們可以知道連接器(Connector)就是按照如此的聲明周期管理的,所以我們找到了線索,所以連接器肯定會先初始化然后再啟動。我們查看其initInternal()方法可以知道連接器初始化做了什么事情,源碼如下:
- @Override
- protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
- super.initInternal();
- if (protocolHandler == null) {
- throw new LifecycleException(
- sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"));
- }
- // Initialize adapter
- adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
- protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
- if (service != null) {
- protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
- }
- // Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default
- if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) {
- setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods());
- }
- if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isInstanceCreated()) {
- throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprListener",
- getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
- }
- if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) {
- throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprLibrary",
- getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
- }
- if (AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() && AprLifecycleListener.getUSEOpenssl() &&
- protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) {
- AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler =
- (AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?>) protocolHandler;
- if (jsseProtocolHandler.issslEnabled() &&
- jsseProtocolHandler.getsslImplementationName() == null) {
- // Openssl is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available
- jsseProtocolHandler.setsslImplementationName(OpensslImplementation.class.getName());
- }
- }
- try {
- protocolHandler.init();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new LifecycleException(
- sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
- }
- }
- }
根據上面源碼,我們發現主要是處理protocolHandler并初始化它,同時我們注意到了protocolHandler 設置了一個適配器,我們看看這個適配器是做啥的,跟蹤源碼如下:
- /**
- * The adapter, used to call the connector.
- *
- *&nbs
網頁題目:查漏補缺:連接器在Tomcat中是如何設計的
瀏覽路徑:http://m.newbst.com/news44/102494.html成都網站建設公司_創新互聯,為您提供搜索引擎優化、App設計、定制網站、網站建設、微信小程序、域名注冊
聲明:本網站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如需處理請聯系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創新互聯
猜你還喜歡下面的內容
- 社交電商為何如此火爆?讀懂這四大優勢:搶占未來先機 2021-02-23
- 網站在建設時 文本該如何排版? 2021-02-23
- 網絡推廣越來越難?未來怎么做好網絡營銷? 2021-02-23
- 5G流量爆發,云計算加速,IDC明顯受益 2021-02-23
- 100元買入域名,三個月后翻了近百倍 2021-02-23
- 小程序為什么吸引巨頭 2021-02-23
- 新建網站如何做SEO優化 2021-02-23

- 從4G到5G,只是網速加快了這么簡單嗎? 2021-02-23
- 企業網站為什么一定要做SEO? 2021-02-23
- 一文讀懂Kafka 2021-02-23
- 云主機選購有訣竅 創新互聯支招 2021-02-23
- 百度站長學院:死鏈提交工具注意事項 2021-02-23
- 使機器學習更容易采用的6種工具 2021-02-23
- 深度解析 Flink 是如何管理好內存的? 2021-02-23
- 擁抱大數據是選擇公有云?還是本地部署? 2021-02-23
- SEO優化中白帽SEO和黑帽SEO的區別 2021-02-23
- 跳出率是什么?如何通過降低跳出率提高排名? 2021-02-23
- 小程序這么火,對企業營銷有哪些優勢呢 2021-02-23
- 企業官網首頁應該怎樣做SEO優化 2021-02-23