Python學習教程:手把手教你使用Flask搭建ES搜索引擎
Elasticsearch 是一個開源的搜索引擎,建立在一個全文搜索引擎庫Apache Lucene? 基礎之上。
在夾江等地區,都構建了全面的區域性戰略布局,加強發展的系統性、市場前瞻性、產品創新能力,以專注、極致的服務理念,為客戶提供成都做網站、成都網站設計 網站設計制作按需網站建設,公司網站建設,企業網站建設,品牌網站設計,營銷型網站建設,外貿網站制作,夾江網站建設費用合理。
那么如何實現 Elasticsearch和 Python 的對接成為我們所關心的問題了 (怎么什么都要和 Python 關聯啊)。視頻教程文末也整理好了!

/Python 交互/
所以,Python 也就提供了可以對接 Elasticsearch的依賴庫。
def __init__(
self, index_type:
str, index_name:
str, ip=
"127.0.0.1"):
#
self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=(
'username',
'password'), port=
9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch(
"localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_name初始化連接一個 Elasticsearch 操作對象。
def __init__(
self, index_type:
str, index_name:
str, ip=
"127.0.0.1"):
#
self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=(
'username',
'password'), port=
9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch(
"localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_name默認端口 9200,初始化前請確保本地已搭建好 Elasticsearch的所屬環境。
根據 ID 獲取文檔數據
def
insert_one
(
self,
doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=
self.index_name, doc_type=
self.index_type, body=doc)
def
insert_array
(
self,
docs: list):
for doc
in
docs:
self.es.index(index=
self.index_name, doc_type=
self.index_type, body=doc)插入文檔數據
def
insert_one
(
self,
doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=
self.index_name, doc_type=
self.index_type, body=doc)
def
insert_array
(
self,
docs: list):
for doc
in
docs:
self.es.index(index=
self.index_name, doc_type=
self.index_type, body=doc)搜索文檔數據
def search(
self, query,
count: int =
30):
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": [
"title",
"content",
"link"]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data =
self.es.search(index=
self.index_name, body=dsl, size=
count)
return match_data
def __search(
self, query: dict,
count: int =
20): #
count: 返回的數據大小
results = []
params = {
'size':
count
}
match_data =
self.es.search(index=
self.index_name, body=query, params=params)
for hit
in match_data['hits']['hits']:
results.append(hit['_source'])
return results刪除文檔數據
def
delete_index
(self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
except:
pass好啊,封裝 search 類也是為了方便調用,整體貼一下。
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
class elasticSearch():
def __init__(
self, index_type:
str, index_name:
str, ip=
"127.0.0.1"):
#
self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=(
'elastic',
'password'), port=
9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch(
"localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_name
def create_index(
self):
if
self.es.indices.exists(index=
self.index_name) is True:
self.es.indices.delete(index=
self.index_name)
self.es.indices.create(index=
self.index_name, ignore=
400)
def delete_index(
self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=
self.index_name)
except:
pass
def get_doc(
self, uid):
return
self.es.get(index=
self.index_name, id=uid)
def insert_one(
self, doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=
self.index_name, doc_type=
self.index_type, body=doc)
def insert_array(
self, docs: list):
for doc
in docs:
self.es.index(index=
self.index_name, doc_type=
self.index_type, body=doc)
def search(
self, query, count: int =
30):
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": [
"title",
"content",
"link"]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data =
self.es.search(index=
self.index_name, body=dsl, size=count)
return match_data嘗試一下把 MongoDB 中的數據插入到 ES 中。
import json
from datetime
import datetime
import pymongo
from app.elasticsearchClass
import elasticSearch
client = pymongo.MongoClient(
'127.0.0.1',
27017)
db = client[
'spider']
sheet = db.get_collection(
'Spider').find({}, {
'_id':
0, })
es = elasticSearch(index_type=
"spider_data",index_name=
"spider")
es.create_index()
for i
in sheet:
data = {
'title': i[
"title"],
'content':i[
"data"],
'link': i[
"link"],
'create_time':datetime.now()
}
es.insert_one(doc=
data)到ES中查看一下,啟動 elasticsearch-head 插件。
如果是 npm 安裝的那么cd到根目錄之后直接npm run start就跑起來了。
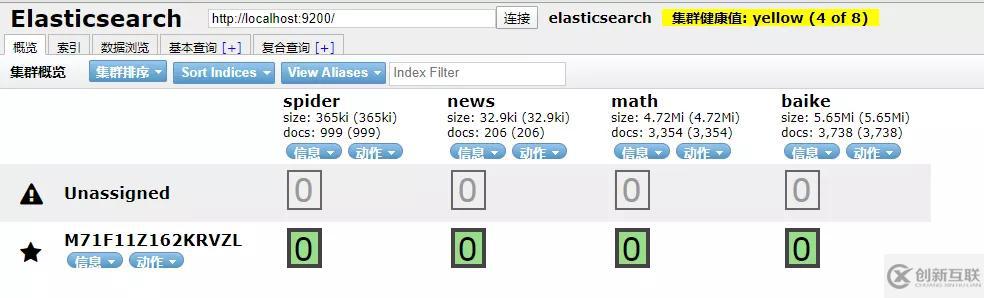
發現新加的 spider 數據文檔確實已經進去了。
/爬蟲入庫/
要想實現 ES 搜索,首先要有數據支持,而海量的數據往往來自爬蟲。
為了節省時間,編寫一個最簡單的爬蟲,抓取 百度百科。
簡單粗暴一點,先 遞歸獲取 很多很多的 url 鏈接
import requests
import re
import time
exist_urls = []
headers = {
'User-Agent':
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/62.0.3202.62 Safari/537.36',
}
def get_link(url):
try:
response = requests.
get(url=url, headers=headers)
response.encoding =
'UTF-8'
html = response.text
link_lists = re.findall(
'.*?<a target=_blank href="/item/([^:#=<>]*?)".*?</a>', html)
return link_lists
except Exception
as e:
pass
finally:
exist_urls.append(url)
# 當爬取深度小于
10層時,遞歸調用主函數,繼續爬取第二層的所有鏈接
def main(start_url, depth=
1):
link_lists = get_link(start_url)
if link_lists:
unique_lists = list(
set(link_lists) -
set(exist_urls))
for unique_url
in unique_lists:
unique_url =
'https://baike.baidu.com/item/' + unique_url
with
open(
'url.txt',
'a+')
as f:
f.write(unique_url +
'\n')
f.close()
if depth <
10:
main(unique_url, depth +
1)
if __name__ ==
'__main__':
start_url =
'https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%99%BE%E5%BA%A6%E7%99%BE%E7%A7%91'
main(start_url)把全部 url 存到 url.txt 文件中之后,然后啟動任務。
# parse.pyfrom celery
import Celery
import requests
from lxml
import etree
import pymongo
app = Celery(
'tasks', broker=
'redis://localhost:6379/2')
client = pymongo.MongoClient(
'localhost',
27017)
db = client[
'baike']
@app.task
def get_url(link):
item = {}
headers = {
'User-Agent':
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/34.0.1847.131 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(link,headers=headers)
res.encoding =
'UTF-8'
doc = etree.HTML(res.text)
content = doc.xpath(
"//div[@class='lemma-summary']/div[@class='para']//text()")
print(res.status_code)
print(link,
'\t',
'++++++++++++++++++++')
item[
'link'] = link
data =
''.join(content).replace(
' ',
'').replace(
'\t',
'').replace(
'\n',
'').replace(
'\r',
'')
item[
'data'] = data
if db[
'Baike'].insert(dict(item)):
print(
"is OK ...")
else:
print(
'Fail')run.py 飛起來
from parse import get_url
def
main(
url):
result = get_url.delay(url)
return
result
def
run(
):
with
open(
'./url.txt',
'r')
as f:
for url
in f.
readlines(
):
main(
url.strip(
'\n'))
if __name__ ==
'__main__':
run()黑窗口鍵入
celery -A parse worker -l info -P gevent -c 10
哦 !! 你居然使用了 Celery 任務隊列,gevent 模式,-c 就是10個線程刷刷刷就干起來了,速度杠杠的 !!
啥?分布式? 那就加多幾臺機器啦,直接把代碼拷貝到目標服務器,通過redis 共享隊列協同多機抓取。
這里是先將數據存儲到了 MongoDB 上(個人習慣),你也可以直接存到 ES 中,但是單條單條的插入速度堪憂(接下來會講到優化,哈哈)。
使用前面的例子將 Mongo 中的數據批量導入到 ES 中,OK !!!
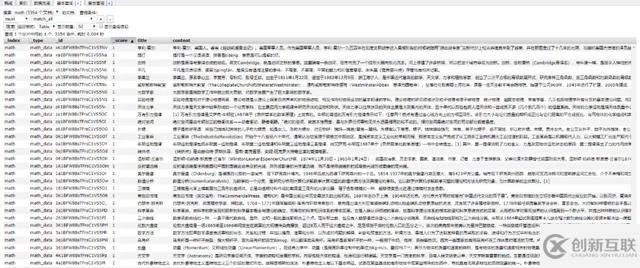
到這一個簡單的數據抓取就已經完畢了。
同學們不清楚的地方,可以留言,更多的教程,也會繼續更新,感謝大家一直以來的支持!
應伙伴們的要求,嘔心瀝血整理了
900集的全套Python學習視頻教程:Python 900集全套視頻教程(全家桶)
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cU5lDWq9gh0cQ7hCnXUiGA
要學習的伙伴們,可以回復:“Python視頻教程”,即可領取!
當前題目:Python學習教程:手把手教你使用Flask搭建ES搜索引擎
本文鏈接:http://m.newbst.com/article34/jesdse.html
成都網站建設公司_創新互聯,為您提供虛擬主機、靜態網站、網站排名、App設計、網站制作、響應式網站
聲明:本網站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如需處理請聯系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創新互聯

- 創新互聯談響應式網站或自適應網站的優點和缺點 2021-10-04
- 自適應網站建設該如何去設置 2013-06-07
- 成都網站建設響應式網站、自適應網站以及H5網站之間區別 2016-09-29
- 自適應網站優化時的優缺點解析! 2022-10-17
- 自適應網站建設要注意哪些問題?自適應網站建設要注意哪幾點 2016-09-01
- 上海自適應網站建設要注意什么? 2020-12-28
- 【成都網站建設】自適應網站和響應式網站之間的區別? 2013-07-27
- 解讀自適應網站有哪些優缺點 2023-01-26
- 自適應網站建設方案 2021-05-15
- 羅湖網站建設:自適應網站有哪些優點? 2022-12-22
- 成都網站建設:自適應網站和響應式網站建設需要注意什么? 2017-01-10
- 企業網站制作為什么要做手機站自適應網站又有什么優勢 2021-08-30